Maltodextrin is a food additive derived from starch, and is found in a variety of packaged and processed foods. It can also be in vitamins and sugar substitutes. It is one of many food additives derived from natural or organic sources that undergoes significant processing to reach its usable form. Because of how it is made, it is impossible to find in a naturally occurring state. It is almost always added to processed foods for various reasons.
What Is Maltodextrin?
Maltodextrin comes in the form of a white powder or a concentrate. It is typically derived from starches such as rice, corn and potato in the USA, and wheat or barley in Europe. The starch is cooked with acid or enzymes to replicate the way that digestion breaks down starch. It is considered a simple sugar and described as “not sweet” by the FDA. However, the flavor is reported as anywhere from slightly sweet to completely devoid of flavor. Maltodextrin is sometimes confused with maltose because of the similar names, however, it does not contain maltose.
Where Is Maltodextrin Found?
Maltodextrin is often found just like sugar in a variety of packaged and processed foods. Common places to find the additive includes cereals, packaged cookies, potato chips, powdered drink mixes, sodas, instant soup mixes, sports drinks and vitamins. It also commonly appears in sugar substitutes such as Splenda. Using the Splenda example, this sweetener is almost completely maltodextrin because it uses sucralose, which is much sweeter than sugar. Because maltodextrin is essentially a sugar, sweeteners such as Splenda are not actually sugar free.
Maltodextrin Uses
Maltodextrin is used as a binder, a filler and a sweetener, depending on the food or product it is used in. In the case of savory foods such as potato chips, it is used to impart a slightly sweet taste, which can help the food be more addictive. It can also be used as a filler or thickener because it is more or less flavorless and will not alter the flavor of most foods. The binder use is mostly in vitamins and drugs, both powdered and solid.
Maltodextrin Side Effects
Despite the fact that this compound is essentially organic, it is still artificially processed and separated from its natural location. It is also a carbohydrate and possesses a high glycemic index, making it unsuitable for those struggling with diabetes or high blood sugar. Similar health side effects to other sugars have been observed. This includes weight gain, high blood sugar and metabolic syndrome. Side effects related to consumption are also similar to general carbohydrate intolerance. These may include stomach upset, vomiting, asthma, rashes, hives and bowel issues.
Is Maltodextrin Gluten Free?
Because it is highly processed food additive, the source of this compound does not factor into its relationship with gluten. It is essentially gluten free, however, many people have reported similar reactions to gluten allergies. According to FDA labeling procedures, it is considered gluten free.

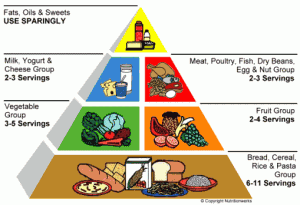 Healthy eating includes a variety of foods that gives your body the right amount of nutrients you need to maintain your health, give you energy and make you feel good. It’s important to eat three meals and three snacks a day. Another way to approach it is to eat six small meals a day.
Healthy eating includes a variety of foods that gives your body the right amount of nutrients you need to maintain your health, give you energy and make you feel good. It’s important to eat three meals and three snacks a day. Another way to approach it is to eat six small meals a day.